The Importance of Recognising and Responding to Head Injuries
Head injuries can happen anywhere! We often ask; can head injuries and concussions be deadly? While a head injury can happen at home, in the workplace, on the sports field, or even during everyday activities sometimes they can be serious.
While some knocks to the head may seem minor, others can lead to serious complications, including concussions or brain injuries. Recognising the signs of a head injury and knowing how to respond can make a crucial difference in preventing long-term damage.
Read on to understand the different types of head injuries, how to identify a concussion, and the essential first aid steps to take. Whether it’s a child who’s fallen on the playground, an employee who’s suffered a workplace accident, or a loved one involved in a collision, understanding head injury first aid is a vital skill that everyone should have.
Famous People Who Suffered Severe or Fatal Head Injuries
-
Natasha Richardson (1963–2009) – The actress, best known for The Parent Trap, suffered a seemingly minor head injury while skiing in Canada. Initially, she felt fine and even declined medical attention, but hours later, she developed a severe headache due to an epidural hematoma (bleeding in the brain). She tragically passed away two days later, highlighting how delayed symptoms of head injuries can be deadly.
-
Michael Schumacher (1969–Present) – The legendary Formula 1 driver suffered a severe traumatic brain injury while skiing in 2013. Despite wearing a helmet, he hit his head on a rock, leading to extensive brain damage. After multiple surgeries and years of rehabilitation, his condition remains largely private, but he has required ongoing medical care.
-
Gary Busey (1944–Present) – The actor, famous for roles in Point Break and Lethal Weapon, suffered a near-fatal motorcycle accident in 1988. He was not wearing a helmet and sustained a severe traumatic brain injury. His personality and cognitive functions were reportedly affected, showing how head injuries can have lasting consequences.
-
Bob Saget (1956–2022) – The Full House actor and comedian died unexpectedly in a hotel room, and an autopsy later revealed he had suffered a significant head injury, likely from a fall. His case serves as a reminder that even seemingly mild head trauma can be fatal if left untreated.
-
Liam Neeson (Connection to Natasha Richardson) – While Liam Neeson himself hasn’t suffered a serious head injury, his wife’s tragic passing (Natasha Richardson) deeply affected him. He later advocated for greater awareness of head trauma and the importance of seeking medical attention after a fall or impact.
These cases demonstrate that head injuries should never be underestimated, even if symptoms don’t appear immediately.
Types of Head Injuries – Can Head Injuries and Concussions be Deadly?
Minor Head Injuries Minor head injuries are common and often result from everyday accidents like bumps, falls, or low-impact collisions. While they typically cause only temporary discomfort, such as mild headaches, dizziness, or swelling, it’s still important to monitor for any worsening symptoms. Applying a cold compress, resting, and staying hydrated can help with recovery. However, even a seemingly minor injury can occasionally lead to complications, so if symptoms like persistent headaches, nausea, slurred words, drowsiness or confusion develop, medical attention should be sought. Being aware of the signs and providing proper care ensures that minor head injuries don’t turn into more serious health concerns.
Concussions A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury caused by a sudden impact or jolt to the head, shaking the brain inside the skull. While often not life-threatening, concussions can have serious effects on cognitive function, balance, and memory. Symptoms may appear immediately or develop hours later, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, and sensitivity to light or noise. Rest and reduced mental strain are crucial for recovery, as pushing through symptoms can prolong healing. Though most concussions resolve within a few weeks, repeated head injuries can have long-term consequences, making proper care and medical evaluation essential.
Skull Fractures A skull fracture is a serious head injury that occurs when there is a break in the skull bone, often caused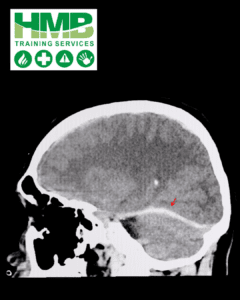 by a heavy impact, fall, or direct blow to the head. Unlike minor head injuries, skull fractures can lead to complications such as brain injuries, internal bleeding, or infection. Symptoms may include a visible wound, swelling, severe headache, nausea, dizziness, confusion, or clear fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) leaking from the nose or ears. In some cases, bruising around the eyes or behind the ears, known as “raccoon eyes” and “Battle’s sign,” can indicate a more severe injury. Immediate medical attention is essential, as untreated skull fractures can lead to serious complications, including brain damage.
by a heavy impact, fall, or direct blow to the head. Unlike minor head injuries, skull fractures can lead to complications such as brain injuries, internal bleeding, or infection. Symptoms may include a visible wound, swelling, severe headache, nausea, dizziness, confusion, or clear fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) leaking from the nose or ears. In some cases, bruising around the eyes or behind the ears, known as “raccoon eyes” and “Battle’s sign,” can indicate a more severe injury. Immediate medical attention is essential, as untreated skull fractures can lead to serious complications, including brain damage.
Severe Brain Injuries Severe brain injuries, often resulting from significant trauma like a high-impact accident or fall, can cause lasting damage to the brain. These injuries include conditions like brain contusions, haemorrhages, and diffuse axonal injury, where the brain’s structure is disrupted. Symptoms can range from loss of consciousness, severe headaches, confusion, and memory loss, to paralysis, seizures, or changes in speech and behaviour. Severe brain injuries may lead to long-term physical, cognitive, or emotional challenges, requiring extensive medical care and rehabilitation.
Immediate treatment, including stabilising the person, controlling bleeding, and monitoring brain function, is critical to minimizing damage and improving outcomes. If left untreated, severe brain injuries can result in permanent disability or even death.
Signs and Symptoms of a Concussion
A concussion may not always be immediately obvious, so it’s essential to watch for symptoms such as:
- Headache or pressure in the head
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred or double vision
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Confusion or memory problems (e.g., forgetting what happened before or after the injury)
- Slurred speech
- Feeling drowsy or difficulty waking up
- Changes in mood or behaviour (irritability, anxiety, sadness)
Delayed Symptoms – Some concussion symptoms might not appear until hours or days later, such as difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, or persistent headaches. Symptoms may last from a few days to several weeks, with most people recovering within 7–10 days. However, some symptoms, particularly cognitive issues, may persist for weeks or months (post-concussion syndrome). If you are unsure please seek medical advice or visit your A&E.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Help – Can Head Injuries and Concussions be deadly?
While many concussions can be managed with rest and monitoring, seek urgent medical attention if the injured person:
- Becomes unconscious, even for a short time
- Has a severe or worsening headache
- Vomits repeatedly
- Experiences seizures
- Shows signs of weakness, numbness, or coordination problems
- Has one pupil larger than the other
- Becomes extremely drowsy or difficult to wake
First Aid for Head Injuries and Concussions
- Assess the Situation – Check if the person is responsive and breathing. If they are unconscious but breathing normally, place them in the recovery position and call for help.
- Control Any Bleeding – If there is a wound, apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth or bandage. Avoid pressing directly on a suspected skull fracture.
- Keep the Person Still – Encourage the injured person to stay seated or lying down to prevent further injury. Avoid sudden movements.
- Apply a Cold Compress – A wrapped ice pack can help reduce swelling and pain but should never be applied directly to the skin.
- Monitor for Symptoms – Keep an eye on the person for any signs of deterioration over the next 24–48 hours.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Rest and Avoid Screens – Encourage the person to rest, avoid bright lights, and limit screen time.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Light Meals – Drinking water and eating small meals can help with nausea.
- Avoid Strenuous Activities – No sports, heavy lifting, or vigorous activities until cleared by a medical professional.
- Monitor for Worsening Symptoms – If symptoms persist or worsen, seek further medical advice.
What we Train – Can Head Injuries and Concussions be Deadly?
All of our courses are tailored for the group of learners in a fun and friendly way. We consider your start and end times to adapt to your staff schedule. We can add any specifics from your polices, systems of work or previous accidents and risk assessments amendments. On our courses we can add any extra modules or certain previous accidents or near misses. The first aid courses can be adapted to include an element of health and safety. You are really getting a lot for your money and time taking courses with HMB Training Services. Let’s teach you what you need to know before giving CPR.
Emergency First Aid at work;
The Emergency First Aid at Work course is a vital training designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills to handle emergency situations in the workplace. This course provides participants with the knowledge and confidence to effectively respond to injuries, illnesses, and accidents that may occur on-site. Covering topics such as assessing and managing incidents, CPR, choking, bleeding control, and more. The Emergency First Aid at Work course ensures that attendees are prepared to provide immediate and appropriate assistance until professional medical help arrives. This comprehensive training is essential for creating a safe and prepared work environment, where employees can confidently handle emergencies and potentially save lives.
First Aid at Work;
The First Aid at Work course is a comprehensive training course designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively respond to a wide range of medical emergencies in the workplace. This course goes beyond basic first aid training and covers topics such as assessing and managing incidents, CPR and AED usage, treating various injuries and illnesses, dealing with trauma, and more. Participants will learn how to handle emergency situations calmly and efficiently, ensuring the well-being of their colleagues and reducing the risk of further harm. The First Aid at Work course is essential for designated workplace first aiders, supervisors, and anyone responsible for the health and safety of employees. By completing this course, individuals can play a crucial role in promoting a safe and prepared work environment, where prompt and effective first aid can make a significant difference in saving lives and minimising the impact of injuries or illnesses.
Why is it vital to know how to administer First Aid
- Reduce accidents and injuries in your workplace
- Quick reaction and speed in administrating first aid will help save lives
- Reduce the number of incidents by sufficient trained first aiders
- Become more confident and knowledgeable in treating someone
- Increases safety within the workplace; having first aid training promotes a sense of safety and well-being
- Reduce the cost to the employer; reduce staff absences and fines from HSE
- First aid Training is a form of team-building activity
If you are looking to learn more about Can Head Injuries and Concussions be deadly? or first aid training courses click here
Additionally, please do call us on 01543 453338 to see how we can help with delivering group training courses




