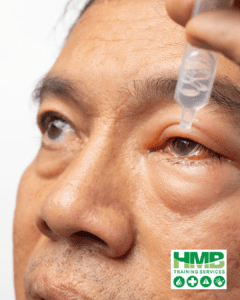
Would you know how to treat eye injuries?
Could you identify if an eye injury is severe and needs hospital treatment?
Eye injuries can happen suddenly and may cause discomfort, vision problems, or even long-term damage if not treated properly. Two common types of eye injuries involve foreign objects (such as dust, sand, or debris) and chemical exposure (from household cleaners, industrial chemicals, or irritants like pepper spray). Knowing how to respond quickly and correctly can help prevent serious complications.
Foreign Objects in the Eye
The eyes are incredibly sensitive, and even the smallest foreign particle can cause discomfort. Common irritants include dust, sand, makeup, metal shavings, wood splinters, and plant material. While minor irritants may be easily flushed out, sharp or embedded objects pose a greater risk and can lead to corneal abrasions, infections, or even permanent damage if not handled correctly.
Symptoms of a Foreign Object in the Eye
- Immediate tearing and watering of the eye (a natural response to flush out the object)
- A gritty or scratchy sensation
- Redness and irritation
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision or difficulty keeping the eye open
- Pain or discomfort when blinking
What to Do; How to Treat Eye Injuries
-
Do Not Rub the Eye
- Rubbing the eye can push the object deeper, cause scratches (corneal abrasions), or lead to infection. Even if the object is small, it’s best to let natural tears or flushing remove it.
-
Blink Several Times
- Rapid blinking can help the eye naturally expel small particles like dust or eyelashes. Tears may help carry the object to the corner of the eye, where it can be wiped away with a clean tissue.
-
Use Clean Water or Saline

- If blinking doesn’t remove the object, flush the eye with lukewarm water or a sterile saline solution.
- Methods to rinse the eye effectively:
- Tilt the head so the affected eye is lower than the unaffected one, preventing contamination.
- Use a glass of clean water or an eye cup to gently rinse the eye.
- If available, an eye wash station (commonly found in workplaces and labs) provides a steady stream of sterile water.
-
Check Under the Eyelid
- Sometimes, small particles get trapped under the eyelid, causing persistent irritation.
- Gently pull down the lower eyelid and inspect for debris.
- If needed, lift the upper eyelid over the lower lashes, as blinking in this position may help sweep out the object.
- If visible, try removing the particle with a damp cotton swab or a clean tissue, ensuring it is not sharp or embedded.
-
Seek Medical Help
- If the object remains stuck, is sharp, or causes ongoing pain or vision changes, seek immediate medical attention.
- DO NOT attempt to remove an embedded object yourself, as this could worsen the injury.
- Cover the eye lightly with a sterile dressing (or a clean cloth) and seek an eye specialist or emergency care.
Chemical Exposure to the Eye
Exposure to chemicals can cause serious eye damage, even leading to vision loss if not treated immediately. Common irritants include household cleaning products (bleach, detergents, and ammonia), industrial chemicals, aerosols, and even some personal care products like hairspray or sunscreen. Alkalis (e.g., ammonia, drain cleaners, lime-based products) tend to cause more severe damage than acids (e.g., battery acid, vinegar, or some disinfectants) because they penetrate deeper into the tissues of the eye.
Symptoms of Chemical Exposure in the Eye
- Immediate burning or stinging sensation
- Excessive tearing and redness
- Blurred vision or difficulty keeping the eye open
- Swelling around the eyelids
- Severe pain (especially with alkaline substances)
- White or cloudy patches on the eye, indicating tissue damage (in severe cases)
What to Do:
-
Flush the Eye Immediately
- The most critical first step is continuous flushing of the affected eye for at least 15–20 minutes with clean, lukewarm water or sterile saline solution.
- If only one eye is affected, tilt the head so that the contaminated eye is lower to prevent the chemical from spreading to the other eye.
- If possible, hold the eyelids open with clean fingers to ensure proper rinsing of the entire eye surface.
-
Remove Contact Lenses
- If the person is wearing contact lenses, remove them immediately, as they can trap chemicals against the eye and worsen the injury.
- Do not attempt to reuse the lenses after exposure—dispose of them safely.
-
Seek Emergency Medical Help
- Even if the eye appears better after rinsing, chemical burns require medical evaluation to prevent long-term damage.
- Strong chemicals like bleach, ammonia, or industrial solvents can cause severe burns that continue damaging the eye tissues even after flushing.
- Contact emergency services or an eye specialist as soon as possible.
-
Avoid Rubbing or Applying Ointments
- Rubbing may spread the chemical deeper into the eye.
- Do not apply ointments or drops unless instructed by a healthcare professional, as they may interfere with treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Eye Injuries – How to Treat Eye Injuries
While some minor irritants can be managed at home, medical help should be sought if:
✅ The foreign object is large, sharp, or embedded in the eye.
✅ Pain, redness, or irritation persists after flushing.
✅ There is blurred vision or difficulty seeing.
✅ A chemical exposure involves strong acids, alkalis, or toxic substances.
✅ The injured person has eye bleeding, pus discharge, or swelling that worsens.
What we Train – How to Treat Eye Injuries
All of our courses are tailored for the group of learners in a fun and friendly way. We consider your start and end times to adapt to your staff schedule. We can add any specifics from your polices, systems of work or previous accidents and risk assessments amendments. On our courses we can add any extra modules or certain previous accidents or near misses. The first aid courses can be adapted to include an element of health and safety. You are really getting a lot for your money and time taking courses with HMB Training Services. Let’s teach you what you need to know before giving CPR.
Emergency First Aid at work;
The Emergency First Aid at Work course is a vital training designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills to handle emergency situations in the workplace. This course provides participants with the knowledge and confidence to effectively respond to injuries, illnesses, and accidents that may occur on-site. Covering topics such as assessing and managing incidents, CPR, choking, bleeding control, and more. The Emergency First Aid at Work course ensures that attendees are prepared to provide immediate and appropriate assistance until professional medical help arrives. This comprehensive training is essential for creating a safe and prepared work environment, where employees can confidently handle emergencies and potentially save lives.
First Aid at Work;
The First Aid at Work course is a comprehensive training course designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively respond to a wide range of medical emergencies in the workplace. This course goes beyond basic first aid training and covers topics such as assessing and managing incidents, CPR and AED usage, treating various injuries and illnesses, dealing with trauma, and more. Participants will learn how to handle emergency situations calmly and efficiently, ensuring the well-being of their colleagues and reducing the risk of further harm. The First Aid at Work course is essential for designated workplace first aiders, supervisors, and anyone responsible for the health and safety of employees. By completing this course, individuals can play a crucial role in promoting a safe and prepared work environment, where prompt and effective first aid can make a significant difference in saving lives and minimising the impact of injuries or illnesses.
Why is it vital to know how to administer First Aid
- Reduce accidents and injuries in your workplace
- Quick reaction and speed in administrating first aid will help save lives
- Reduce the number of incidents by sufficient trained first aiders
- Become more confident and knowledgeable in treating someone
- Increases safety within the workplace; having first aid training promotes a sense of safety and well-being
- Reduce the cost to the employer; reduce staff absences and fines from HSE
- First aid Training is a form of team-building activity
If you are looking to learn more about – How to Treat Eye Injuries or first aid training courses click here
Additionally, please do call us on 01543 453338 to see how we can help with delivering group training courses